How To Create A Rapport
Getting Started
This tutorial walks you through using Amazon Athena to query data. You'll create a table based on sample data stored in Amazon Simple Storage Service, query the table, and check the results of the query.
The tutorial uses live resources, so you are charged for the queries that you run. You aren't charged for the sample data in the location that this tutorial uses, but if you upload your own data files to Amazon S3, charges do apply.
Prerequisites
-
If you have not already done so, sign up for an account in Setting Up.
-
Using the same AWS Region (for example, US West (Oregon)) and account that you are using for Athena, Create a bucket in Amazon S3 to hold your Athena query results.
Step 1: Create a Database
You first need to create a database in Athena.
To create an Athena database
-
Open the Athena console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/athena/
. -
If this is your first time to visit the Athena console in your current AWS Region, choose Explore the query editor to open the query editor. Otherwise, Athena opens in the query editor.
-
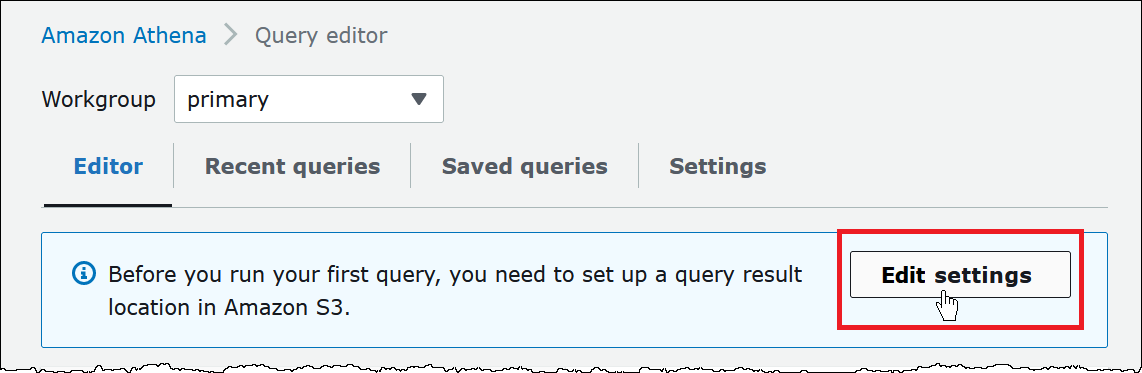
Choose View Settings to set up a query result location in Amazon S3.
-
On the Settings tab, choose Manage.

-
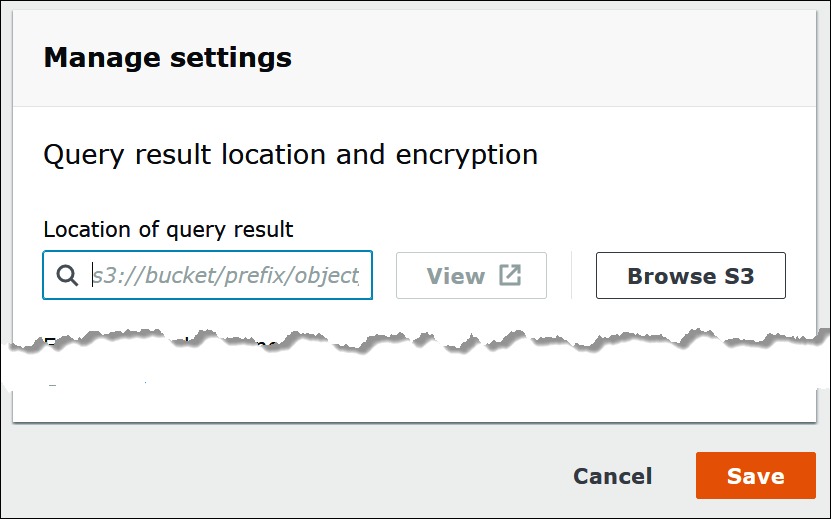
For Manage settings, do one of the following:
-
In the Location of query result box, enter the path to the bucket that you created in Amazon S3 for your query results. Prefix the path with
s3://. -
Choose Browse S3, choose the Amazon S3 bucket that you created for your current Region, and then choose Choose.
-
-
Choose Save.
-
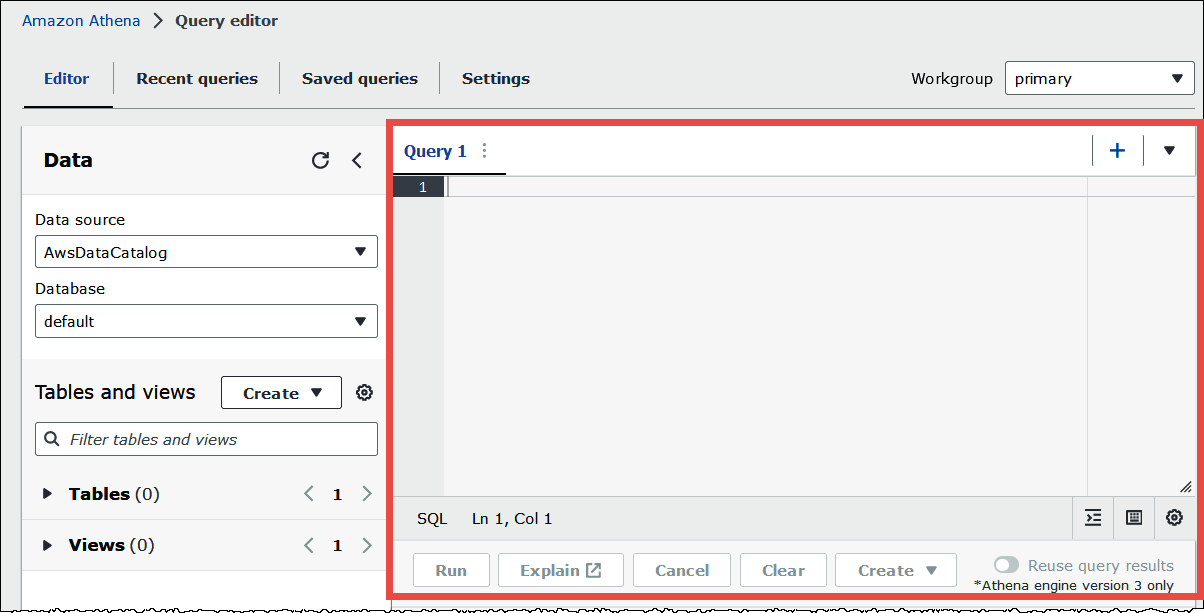
Choose Editor to switch to the query editor.

-
On the right of the navigation pane, you can use the Athena query editor to enter and run queries and statements.
-
To create a database named
mydatabase, enter the following CREATE DATABASE statement.CREATE DATABASE mydatabase -
Choose Run or press
Ctrl+ENTER. -
From the Database list on the left, choose
mydatabaseto make it your current database.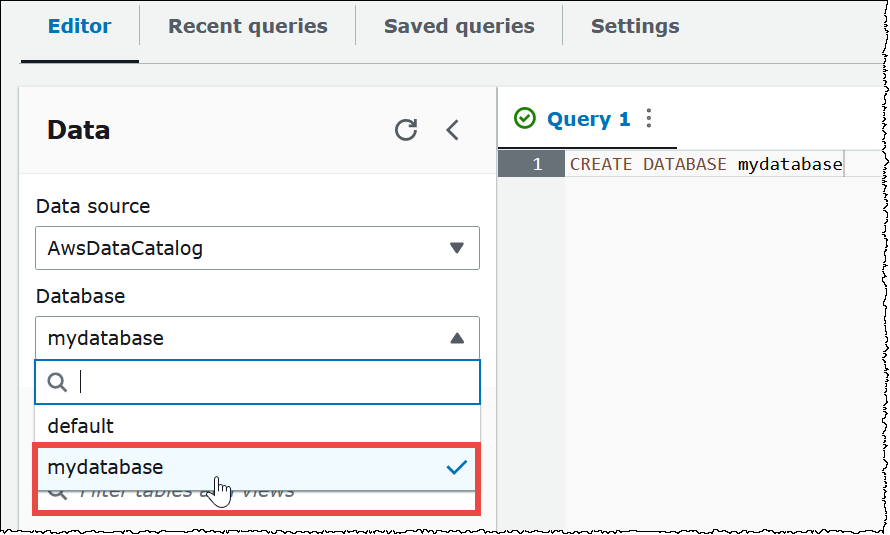
Step 2: Create a Table
Now that you have a database, you can create an Athena table for it. The table that you create will be based on sample Amazon CloudFront log data in the location s3://athena-examples-, where myregion/cloudfront/plaintext/myregion is your current AWS Region.
The sample log data is in tab-separated values (TSV) format, which means that a tab character is used as a delimiter to separate the fields. The data looks like the following example. For readability, the tabs in the excerpt have been converted to spaces and the final field shortened.
2014-07-05 20:00:09 DFW3 4260 10.0.0.15 GET eabcd12345678.cloudfront.net /test-image-1.jpeg 200 - Mozilla/5.0[...] 2014-07-05 20:00:09 DFW3 4252 10.0.0.15 GET eabcd12345678.cloudfront.net /test-image-2.jpeg 200 - Mozilla/5.0[...] 2014-07-05 20:00:10 AMS1 4261 10.0.0.15 GET eabcd12345678.cloudfront.net /test-image-3.jpeg 200 - Mozilla/5.0[...] To enable Athena to read this data, you could run a CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE statement like the following. The statement that creates the table defines columns that map to the data, specifies how the data is delimited, and specifies the Amazon S3 location that contains the sample data.
For the LOCATION clause, specify an Amazon S3 folder location, not a specific file. Athena scans all of the files in the folder that you specify.
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE IF NOT EXISTS cloudfront_logs ( `Date` DATE, Time STRING, Location STRING, Bytes INT, RequestIP STRING, Method STRING, Host STRING, Uri STRING, Status INT, Referrer STRING, ClientInfo STRING ) ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t' LINES TERMINATED BY '\n' LOCATION 's3://athena-examples-my-region/cloudfront/plaintext/'; The example creates a table called cloudfront_logs and specifies a name and data type for each field. These fields become the columns in the table. Because date is a reserved word, it is escaped with backtick (`) characters. ROW FORMAT DELIMITED means that Athena will use a default library called LazySimpleSerDe to do the actual work of parsing the data. The example also specifies that the fields are tab separated (FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t') and that each record in the file ends in a newline character (LINES TERMINATED BY '\n). Finally, the LOCATION clause specifies the path in Amazon S3 where the actual data to be read is located. If you have your own tab or comma-separated data, you can use a CREATE TABLE statement like this.
Returning to the sample data, here is a full example of the final field ClientInfo:
Mozilla/5.0%20(Android;%20U;%20Windows%20NT%205.1;%20en-US;%20rv:1.9.0.9)%20Gecko/2009040821%20IE/3.0.9 As you can see, this field is multivalued. If the CREATE TABLE statement specifies tabs as field delimiters, the separate components inside this particular field can't be broken out into separate columns. To create columns from the values inside the field, you can use a regular expression (regex) that contains regex groups. The regex groups that you specify become separate table columns. To use a regex in your CREATE TABLE statement, use syntax like the following. This syntax instructs Athena to use the Regex SerDe library and the regular expression that you specify.
ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.RegexSerDe' WITH SERDEPROPERTIES ("input.regex" = "regular_expression") Regular expressions can be useful for creating tables from complex CSV or TSV data but can be difficult to write and maintain. Fortunately, there are other libraries that you can use for formats like JSON, Parquet, and ORC. For more information, see Supported SerDes and Data Formats.
Now you are ready to create the table in the Athena query editor. The CREATE TABLE statement and regex are provided for you.
To create a table in Athena
-
In the navigation pane, for Database, make sure that
mydatabaseis selected. -
To give yourself more room in the query editor, you can choose the arrow icon to collapse the navigation pane.
-
To create a tab for a new query, choose the plus (+) sign in the query editor. You can have up to ten query tabs open at once.
-
In the query pane, enter the following
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLEstatement. The regex breaks out the operating system, browser, and browser version information from theClientInfofield in the log data.CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE IF NOT EXISTS cloudfront_logs ( `Date` DATE, Time STRING, Location STRING, Bytes INT, RequestIP STRING, Method STRING, Host STRING, Uri STRING, Status INT, Referrer STRING, os STRING, Browser STRING, BrowserVersion STRING ) ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.RegexSerDe' WITH SERDEPROPERTIES ( "input.regex" = "^(?!#)([^ ]+)\\s+([^ ]+)\\s+([^ ]+)\\s+([^ ]+)\\s+([^ ]+)\\s+([^ ]+)\\s+([^ ]+)\\s+([^ ]+)\\s+([^ ]+)\\s+([^ ]+)\\s+[^\(]+[\(]([^\;]+).*\%20([^\/]+)[\/](.*)$" ) LOCATION 's3://athena-examples-myregion/cloudfront/plaintext/'; -
In the
LOCATIONstatement, replacemyregionwith the AWS Region that you are currently using (for example,us-west-1). -
Choose Run.
The table
cloudfront_logsis created and appears under the list of Tables for themydatabasedatabase.
Step 3: Query Data
Now that you have the cloudfront_logs table created in Athena based on the data in Amazon S3, you can run SQL queries on the table and see the results in Athena. For more information about using SQL in Athena, see SQL Reference for Amazon Athena.
To run a query
-
Choose the plus (+) sign to open a new query tab and enter the following SQL statement in the query pane.
SELECT os, COUNT(*) count FROM cloudfront_logs WHERE date BETWEEN date '2014-07-05' AND date '2014-08-05' GROUP BY os -
Choose Run.
The results look like the following:

-
To save the results of the query to a
.csvfile, choose Download results.
-
To view or run previous queries, choose the Recent queries tab.

-
To download the results of a previous query from the Recent queries tab, select the query, and then choose Download results. Queries are retained for 45 days.

For more information, see Working with Query Results, Recent Queries, and Output Files.
Connecting to Other Data Sources
This tutorial used a data source in Amazon S3 in CSV format. For information about using Athena with AWS Glue, see Using AWS Glue to Connect to Data Sources in Amazon S3. You can also connect Athena to a variety of data sources by using ODBC and JDBC drivers, external Hive metastores, and Athena data source connectors. For more information, see Connecting to Data Sources.
How To Create A Rapport
Source: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/athena/latest/ug/getting-started.html
Posted by: jamesinaboust.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create A Rapport"
Post a Comment